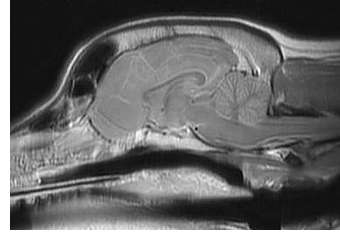
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a strong magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses to change the polarity of hydrogen atoms within cells. A computer monitors the changes of the atoms to create images of fluid, soft tissue and bones. The images produced are similar to computed tomography (see CT vs MRI) but provide greater detail of soft tissues such as the brain, spinal cord, tendons and ligaments. This extra detail is important to identify subtle neurological abnormalities and to clearly distinguish normal tissue from abnormal tissue, especially prior to surgery.
General anesthesia is administered in order to keep patients motionless during the study and technicians skilled in monitoring provide close attention to the patient throughout the procedure. In many cases, a contrast agent (dye) is injected into the patient’s bloodstream to improve the visibility of certain structures. Patients undergoing a spinal MRI usually have survey radiographs taken before the MRI. To help identify metallic structures embedded under the skin (e.g. staples, ID chips, etc), all clients are asked to fill out an MRI Screening Form (part of the Patient Registration Forms). If an MRI is performed, the client’s input on this form will allow the MRI technician to make necessary imaging adjustments to avoid artifacts that could distort the quality of the images.
►Click here to learn more about magnetic resonance imaging.
This information is meant to be a guide and not a substitute for veterinary care.
Always follow the instructions provided by your veterinarian.
Diagnostic Uses of MR Imaging:
Brain:
- tumors
- hydrocephalus
- inflammation (encephalitis, meningitis)
- vascular lesions (stroke or hemorrhage)
Spine
- tumors
- vascular injuries
- intervertebral disk herniations
- infections
- fractures
- dislocations
Non-Neurological Imaging
